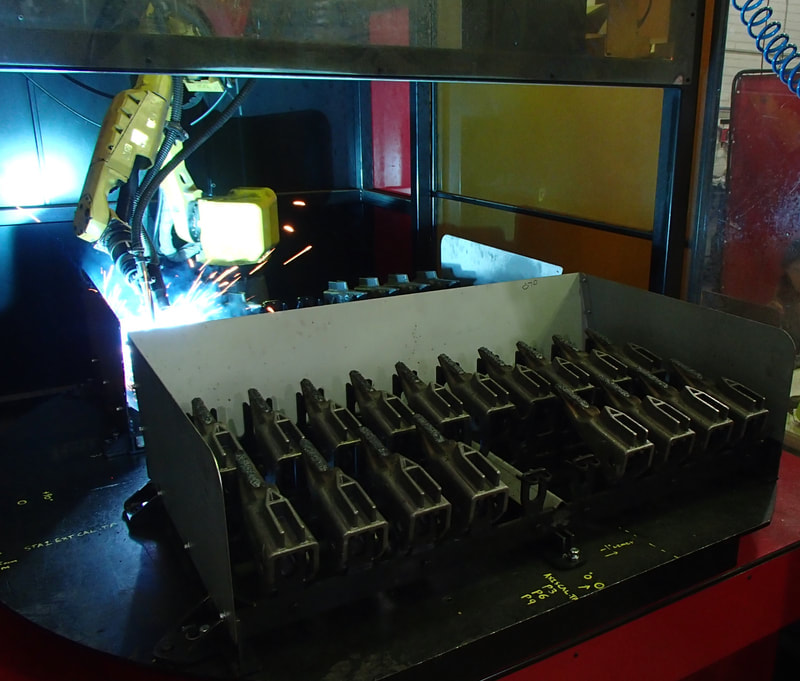
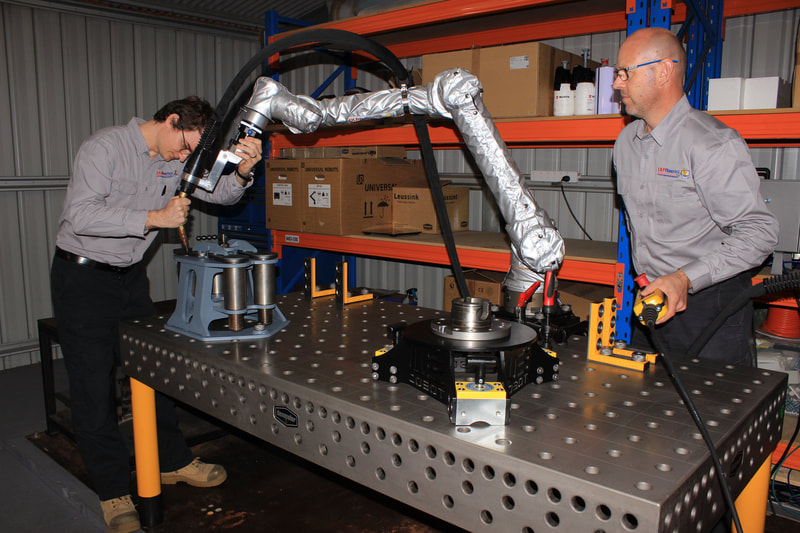
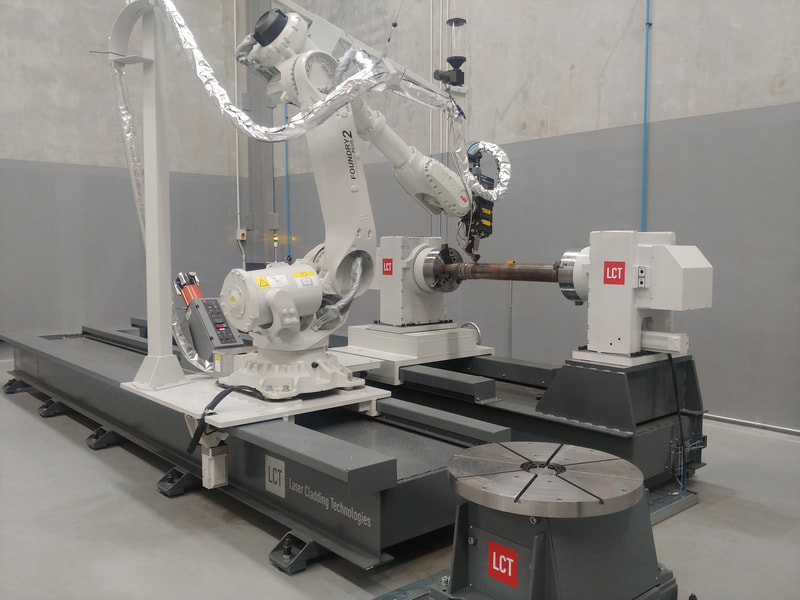
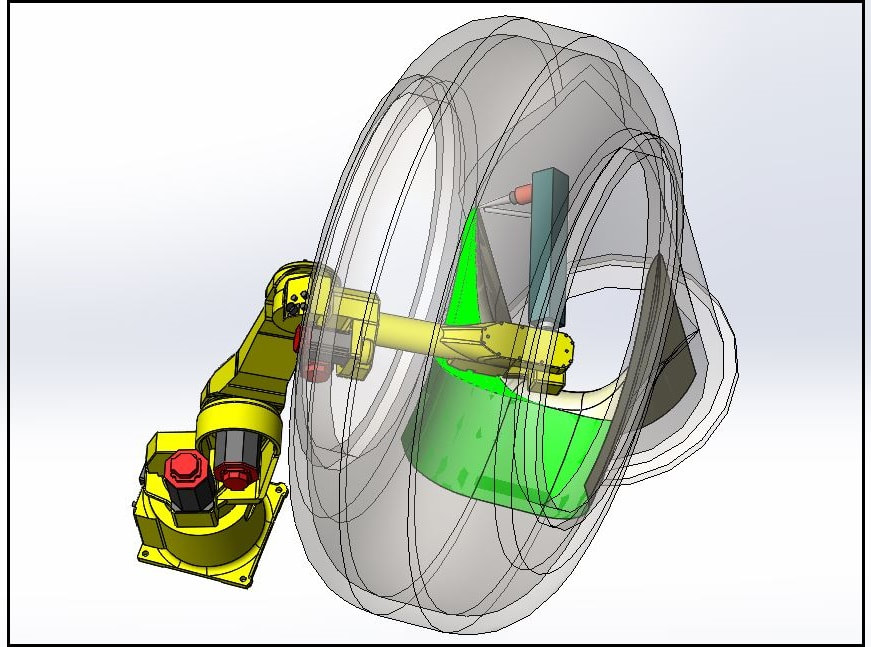
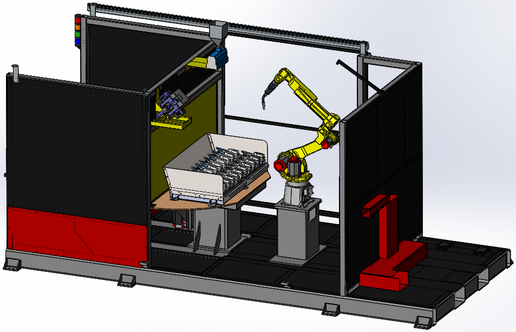
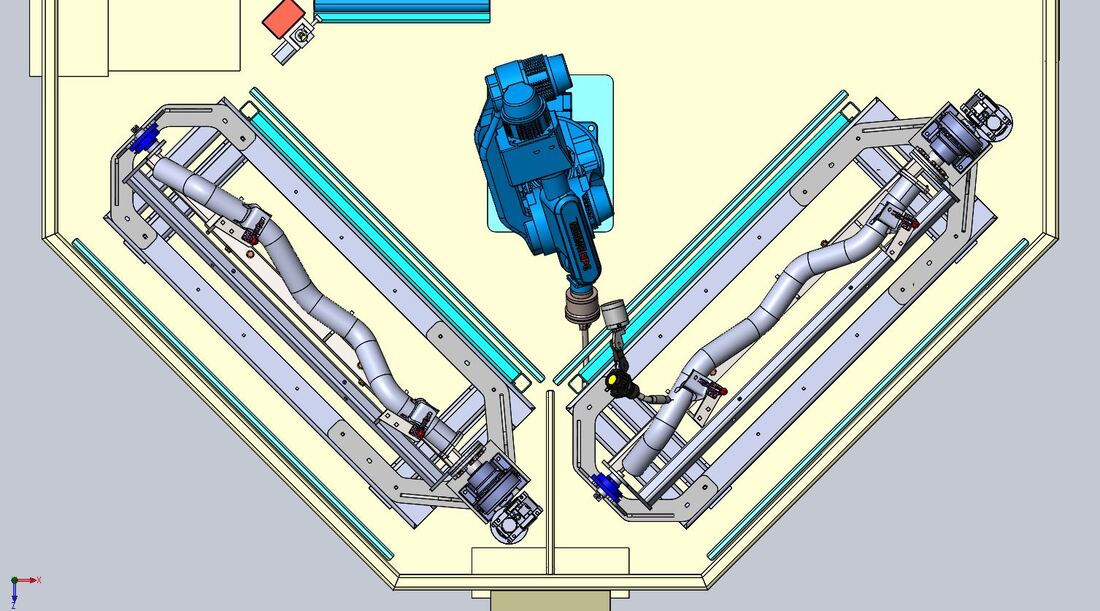
OLP Robotics specialise in developing customised process automation solutions in consultation with our clients. From concept to complete turnkey system, we take the time to understand our clients visions and process requirements and manage the project through to completion.
|
Automation is suited to many tasks, particularly those that are repetitive, dangerous or critical to quality. Processes that are commonly automated using industrial robots include:
|
Our Approach
Before commencing any detailed design or capital investment, we typically conduct an 'Application Study'. This study forms the pre-engineering phase of a project, including spending time with the client to gain a thorough understanding of their needs and interrogate the existing process details and requirements. Once the scope and needs have been clarified, potential options for automation are investigated and simulated in 3D. This process enables optimal design and equipment selection prior to any fabrication or equipment purchases. It also allows the client to visualise the possibilities, and often results in the generation of new ideas to expand on the capabilities of the automated system. At the end of the Application Study, a comprehensive report and offer for project execution is delivered to the client.
Why are factories automating?
Health and Safety
The main driver for process automation is the health and safety of employees. Many tasks that have traditionally been performed manually are very dangerous or pose health risks. Robots are an ideal solution to mitigate risks when a process involves fast-moving parts, toxic fumes, high temperatures, loud noise, or even repetitive muscle strain.
Productivity
Process automation can have huge benefits to time and cost productivity. After the initial investment there are very little ongoing costs to keep the system running. Time and money is also saved in reduced requirements for technician training for complex jobs where precision or technique is critical to quality. Versatility is also increased as one robot can perform a variety of tasks. With the proper care and maintenance, robots can run almost continuously and can be left unsupervised, reducing production downtime during shift changeovers, break times or leaves of absence.
Coupled with offline programming software, new jobs can be programmed quickly and efficiently, without having to stop current production. Efficient motion is also mathematically calculated to reduce time and material wastage.
When the time comes to expand production capability, automated processes are easily scalable. By duplicating work cell setups, programming time is reduced as the same program files can be loaded onto multiple robots.
Quality
The key to a successful business is reputation. In manufacturing companies this is based on customer perception which is driven by consistently high product quality. Whilst many machine operators are very skilled at what they do, there will always be variation between operators and occasional operator error, especially when performing a job for the first time or with long gaps between jobs. Automation mitigates these issues by ensuring mathematically precise, repeatable quality every time, no matter how much time has lapsed between certain tasks.
The main driver for process automation is the health and safety of employees. Many tasks that have traditionally been performed manually are very dangerous or pose health risks. Robots are an ideal solution to mitigate risks when a process involves fast-moving parts, toxic fumes, high temperatures, loud noise, or even repetitive muscle strain.
Productivity
Process automation can have huge benefits to time and cost productivity. After the initial investment there are very little ongoing costs to keep the system running. Time and money is also saved in reduced requirements for technician training for complex jobs where precision or technique is critical to quality. Versatility is also increased as one robot can perform a variety of tasks. With the proper care and maintenance, robots can run almost continuously and can be left unsupervised, reducing production downtime during shift changeovers, break times or leaves of absence.
Coupled with offline programming software, new jobs can be programmed quickly and efficiently, without having to stop current production. Efficient motion is also mathematically calculated to reduce time and material wastage.
When the time comes to expand production capability, automated processes are easily scalable. By duplicating work cell setups, programming time is reduced as the same program files can be loaded onto multiple robots.
Quality
The key to a successful business is reputation. In manufacturing companies this is based on customer perception which is driven by consistently high product quality. Whilst many machine operators are very skilled at what they do, there will always be variation between operators and occasional operator error, especially when performing a job for the first time or with long gaps between jobs. Automation mitigates these issues by ensuring mathematically precise, repeatable quality every time, no matter how much time has lapsed between certain tasks.